What is Regenerative Braking?
If you’ve been considering whether to make the switch to an EV, it’s a good idea to have some knowledge about basic principles of their operation.
EV’s may for the most part appear very similar to ICE (internal combustion engine) cars, but in various aspects, they differ greatly.
You may have heard of the term regenerative braking before, which is integral in such vehicles.
So what is regenerative braking and why is it so integral to EV’s?
Chapters
What is Regenerative Braking?
In a nutshell, regenerative braking means turning your vehicle’s kinetic energy into electricity.
In turn, this will assist with charging the vehicle’s battery while also boosting efficiency.
When the brake pedal is pushed while driving a fuel powered car, the energy simply slows down the car, and the friction and heat that get generated are essentially lost.
All that happens in reality is that they cause wear and tear of the brake pads and discs.
On the other hand, regenerative braking harnesses that energy in an efficient way.
Apart from slowing the vehicle down, the energy is converted into electricity for recharging purposes.
Hence the energy is efficiently recycled.
Brief History of Regenerative Braking
Incredibly, regenerative braking dates back to as early as the year 1886.
The Sprague Electric Railway & Motor Company had developed a drive motor in the front wheels of the Krieger electric landaulet which operated with such a system.
Later on this system was introduced by tram operators in England.
Regenerative braking was used extensively on railroads for several decades.
Improvements in electronics helped the system to advance further over the years.
The process was fully automated in the AMC Amitron experimental electric car back in 1967.
Over time regenerative braking started to be used in electric cars, and many modern hybrids and EVs now use this system to extend the battery range and benefit from this system.
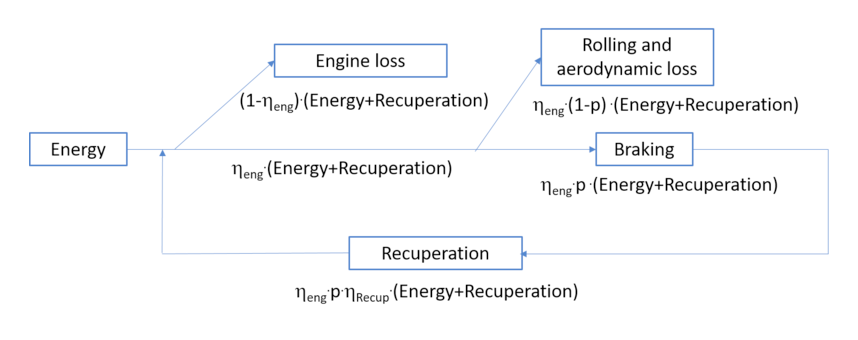
How Does It Work?
When the accelerator pedal is pressed, the motor will have the wheels move in a forward direction.
Then, as the foot is lifted off the accelerator pedal, the momentum turns the motor into a generator.
This induces a current, which is fed back to the car’s battery for recharging purposes.
When the brake pedal is pressed, there will be an increase in the electrical resistance of the motor, which in turn slows down the car.
At the same time, the battery is topped up as there will be more current generated in the process.
These boosts in the battery range will accumulate and in time improve the efficiency.
How Regenerative Brakes Feel vs Conventional Brakes
All cars have conventional friction brakes.
But in the case of electric vehicles, the brakes can feel a little different, especially when lifting off the accelerator but not actually pressing the brake pedal itself.
In such cases, lifting off the accelerator creates a sense of drag, with the vehicle actually slowing down as opposed to coasting as it would in a traditional petrol or diesel vehicle.
But in cases where the brake pedal is depressed and used to stop the vehicle, the difference in sensation between an EV or an ICE is negligible.
In the case of an emergency stop, if the pedal is pressed hard, the hydraulic system will kick into action to slow the car down as quickly as possible, whether an EV or an ICE.
The amount of force required on the pedals may vary from one car model to another.
Indeed, the sensation that the car is slowing down will not be the same for every car.
There are vehicles which allow the driver to set the strength of the regenerative braking system either by means of the menu or through paddles that are attached to the steering wheel.
Other cars will be pre-programmed as to how much regenerative braking will occur when the force on the pedal is lifted off.
Advantages of Regenerative Braking
Brake Pad & Rotor Life
Brake pads and rotors show wear quite quickly in cars that operate with traditional friction brakes.
Regenerative brakes do not have this problem, and many EVs and hybrids generally go around 100,000 miles without having to undergo brake servicing, unlike fuel powered cars.
Recovered Energy
As noted before, hydraulic brakes will waste the energy that arises from kinetic energy to heat energy.
On the other hand, regenerative braking will utilise that energy efficiently by feeding it into the car battery.
Hence, extended driving range will be gained.
Extended Range
Even though regenerative braking is not going to add a lot of miles to the driving range, it’s still a plus since the recaptured energy will add up, especially if used regularly.
And when it comes to electrical vehicles, every mile of battery range is important.
Improved Fuel Efficiency
Regenerative braking helps to improve fuel efficiency as it ultimately takes some of the load off the motor as some auxiliary functions of the car can be powered by this recaptured energy.
Disadvantages of Regenerative Braking
Period of Adjustment
One of the main disadvantages that drivers mention is that there is a period of adjustment as regenerative brakes will need some getting used to.
This is especially true if one has always driven conventional fuel powered cars for many years prior to switching to an EV.
It’s also worth pointing out that while this system is advantageous, it’s still a technology that’s advancing as we speak.
Braking Feels Different
The braking will feel somewhat different from one car model to another.
This is because one car will require a different amount of force on the pedal to get the brake to kick in.
As soon as the regenerative braking process kicks in, the driver will feel that the car is slowing down, but the sensation will vary from one vehicle to another.
In many EVs, as soon as the driver lifts his foot off the pedal completely it feels as if the brake was pressed firmly.
This is sometimes referred to as one-pedal driving, and it is best to learn how to modulate the right foot to increase speed and to slow down, rather than swapping between pedals.
Less Effective at Low Speeds
Regenerative braking can be somewhat inefficient when driving at low speeds, such as in cities.
This is because the system will not be able to generate enough energy to make a significant impact on the car’s range.
So regenerative braking is less effective if you drive mostly at low speeds.
Less Stopping Power
Regenerative braking is not that reliable if you are driving at considerably high speeds.
Unlike friction braking, when the driver slams on the brakes, the car will stop quickly and this is a reliable system.
Regenerative brakes cannot be said to be as reliable as friction brakes in this regard, especially when it comes to emergency stopping.
In fact, this is one of the main reasons why hybrids and EVs use both types of braking systems.
Conclusion
There is no denying that regenerative brakes are a good way to preserve an EV’s range and improve on its efficiency.
A considerable amount of energy can be recaptured and reutilised, and there are various benefits associated with such a system.
Blog Archive
- Vehicle to Load (V2L): What It Is & How It Works
- 16 Top Charge Point Operators in the UK
- 8 Types of EV Battery Explained
- Where Can I Charge My Electric Car?
- Electric Car Maintenance and Servicing Guide
- How Often Should I Charge My Electric Car?
- How to Check EV Battery Health
- Do Electric Cars Pay Road Tax?
- October 2024 Budget: Key EV News
- EV vs ICE – Which is Best?
- Should I Charge My EV to 80 or 90 or 100%?
- UK Government Announces Hybrid Sales Allowed Until 2035
- BEV vs PHEV – What’s the Difference?
- Definitely Not A Guru (Jim Starling) Reviews Joosup
- How Long Do Electric Car Batteries Last?
- 25 New Electric Car Brands on UK Roads
- General Election 2024: Major Party Net Zero Policies Compared
- Electric Car Service Costs vs ICE
- CHAdeMO vs CCS – What’s the Difference?
- Mr EV Reviews Joosup