8 Types of EV Battery Explained
Electric vehicles (EVs) are transforming the way we think about transportation, offering a cleaner, greener and better alternatives to traditional petrol and diesel cars.
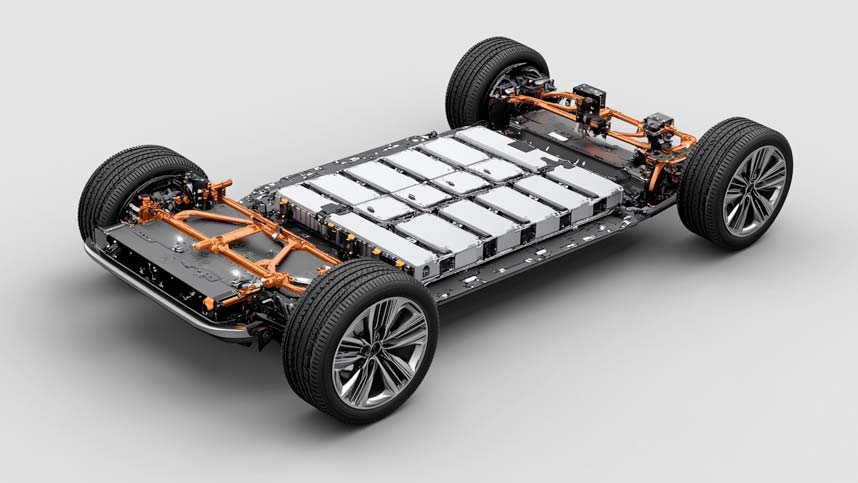
At the heart of every EV lies its type of battery – the powerhouse that determines how far you can go, how quickly and how often you can charge your EV, and how efficiently the vehicle performs.
But not all EV batteries are created equal.
In this article, we’ll explore the different types of EV batteries, their unique characteristics, and what makes them suitable for various applications.
Whether you’re an EV enthusiast or a curious beginner, by the end of this read, you’ll have a clear understanding of the technologies driving the electric revolution.
Chapters
What’s the Purpose of an EV Battery?
Before diving into the specifics, it’s important to understand the role of an EV battery.
Simply put, an EV battery stores electrical energy that powers the vehicle’s electric motor.
Unlike the small 12-volt battery in a conventional ICE car, which is primarily used to start the engine and power accessories, an EV battery is a high-capacity energy storage system designed to deliver sustained power over long distances.
The performance of an EV battery is measured by three key factors:
- Range: How far the vehicle can travel on a single charge.
- Power: How quickly the vehicle can accelerate and maintain speed.
- Capacity: The total amount of energy the battery can store.
These factors are influenced by the battery’s chemistry, design, and manufacturing process.
Let’s take a closer look at the different types of EV batteries available today.
EV Battery Types
1. Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are the most common type of battery used in modern EVs, thanks to their high energy density, long lifespan, and relatively lightweight design.
They come in several variations, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Lithium-NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt)
Lithium-NMC batteries are widely used in EVs due to their balanced performance.
They offer a high energy density, which translates to longer range, and good thermal stability, making them safer than some other chemistries.
However, they rely on cobalt, a material with ethical and environmental concerns due to mining practices.
Advantages
- High energy density
- Good balance of power and range
- Relatively long lifespan
Disadvantages
- Cobalt dependency raises ethical and cost concerns
- Sensitive to high temperatures
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP)
LFP batteries are gaining popularity for their safety, longevity, and lower environmental impact.
They use iron and phosphate instead of cobalt, making them more sustainable and cost-effective.
While they have a slightly lower energy density than NMC batteries, they excel in thermal stability and durability.
Advantages
- Excellent thermal and chemical stability
- Longer lifespan
- Cobalt-free, making them more ethical and affordable
Disadvantages
- Lower energy density, resulting in shorter range
- Heavier than other lithium-ion variants
Lithium Titanate (LTO)
LTO batteries are known for their rapid charging capabilities and exceptional lifespan.
They use titanium in the anode, which allows them to handle high currents without degrading quickly.
However, their lower energy density makes them less suitable for long-range EVs.
Advantages
- Extremely fast charging
- Long cycle life
- Excellent performance in extreme temperatures
Disadvantages
- Lower energy density
- Higher cost
Sodium-Ion
Sodium-ion batteries are an emerging alternative to lithium-ion batteries.
They use sodium, a more abundant and cheaper material, making them a promising option for the future.
While they currently have lower energy density and performance compared to lithium-ion batteries, ongoing research aims to close this gap.
Advantages
- Abundant and inexpensive materials
- Environmentally friendly
Disadvantages
- Lower energy density
- Still in the early stages of commercialisation
2. Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries
Nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries were once the go-to choice for hybrid vehicles like the Toyota Prius.
They offer a good balance of energy density and safety but have largely been replaced by lithium-ion batteries in modern EVs due to their lower efficiency and heavier weight.
Advantages
- Safe and reliable
- Good energy density for hybrids
Disadvantages
- Heavier and bulkier than lithium-ion
- Lower efficiency and shorter lifespan
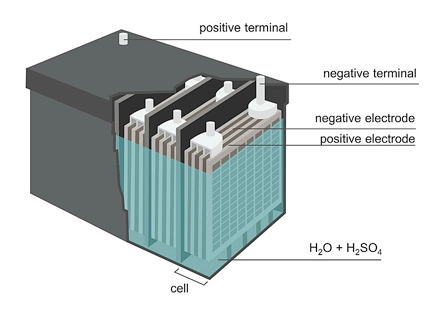
3. Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are one of the oldest rechargeable battery technologies.
While they are cheap and reliable, their low energy density and heavy weight make them unsuitable for modern EVs.
They are occasionally used in low-speed electric vehicles or as auxiliary batteries in EVs.
Advantages
- Low cost
- Proven technology
Disadvantages
- Very low energy density
- Heavy and bulky
- Short lifespan
4. Molten Salt (Zebra) Batteries
Molten salt batteries, also known as sodium-nickel chloride batteries, operate at high temperatures and are primarily used in stationary energy storage systems.
They are not commonly used in EVs due to their complex thermal management requirements.
Advantages
- High energy density
- Long cycle life
Disadvantages
- Requires high operating temperatures
- Complex and costly to maintain
5. Ultracapacitors
Ultracapacitors are not batteries in the traditional sense but are often used alongside them in EVs.
They store energy electrostatically rather than chemically, allowing for rapid charging and discharging.
This makes them ideal for regenerative braking systems and short bursts of power.
Advantages
- Extremely fast charging and discharging
- Long lifespan
Disadvantages
- Low energy density
- Not suitable for long-term energy storage
6. Solid-State Batteries
Solid-state batteries are the next big thing in EV technology.
They replace the liquid electrolyte in traditional lithium-ion batteries with a solid material, offering higher energy density, faster charging, and improved safety.
While still in the development phase, they hold immense promise for the future of EVs.
Advantages
- Higher energy density
- Improved safety
- Faster charging
Disadvantages
- Currently expensive to produce
- Still in the early stages of commercialisation
7. Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries are another emerging technology with the potential to surpass lithium-ion batteries in energy density.
They use sulfur, a lightweight and abundant material, but face challenges with lifespan and stability.
Advantages
- Very high energy density
- Lightweight and cost-effective materials
Disadvantages
- Short lifespan
- Still under development
8. Lithium Manganese Iron Phosphate (LMFP)
LMFP batteries are a newer variant of lithium-ion batteries that combine the benefits of LFP and manganese.
They offer higher energy density than LFP batteries while maintaining good thermal stability and safety.
Advantages
- Higher energy density than LFP
- Good thermal stability
Disadvantages
- Still in the early stages of adoption
- Slightly higher cost than LFP
How are EV Batteries Manufactured?
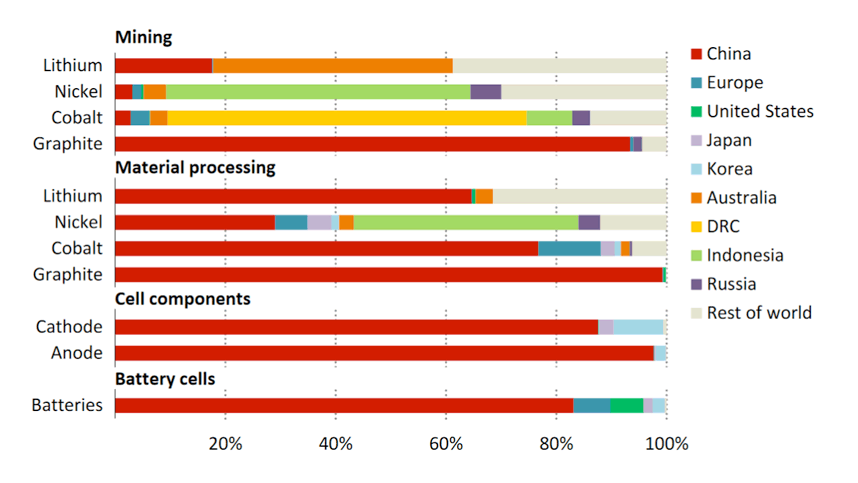
EV battery manufacturing is a complex process that involves sourcing raw materials, assembling cells, and integrating them into battery packs
Key steps include:
- Material Extraction: Mining lithium, cobalt, nickel, and other materials.
- Cell Production: Combining materials into cathodes, anodes, and electrolytes.
- Pack Assembly: Connecting cells into modules and integrating them into a battery pack with cooling and management systems.
Can EV Batteries be Reused or Repurposed?
Yes! EV batteries can be repurposed for secondary applications like energy storage for homes or businesses once they’re no longer suitable for vehicles.
This extends their lifespan and reduces waste.
Can EV Batteries be Recycled?
Absolutely. Recycling EV batteries recovers valuable materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, reducing the need for new mining.
Companies are developing advanced recycling techniques to make this process more efficient and environmentally friendly.
Environmental Considerations
While EVs are cleaner to operate than traditional vehicles, their batteries have environmental impacts, particularly in material extraction and disposal.
However, advancements in recycling, ethical sourcing, and alternative chemistries are helping to mitigate these issues.
Conclusion
The world of EV batteries is diverse and rapidly evolving.
From the widely used lithium-ion batteries to promising newcomers like solid-state and lithium-sulfur, each type has its own strengths and challenges.
As technology advances, we can expect even more efficient, sustainable, and affordable batteries to power the future of transportation.
Whether you’re considering buying an EV or simply curious about the technology, understanding these batteries is key to appreciating the electric revolution.
Blog Archive
- Solid State EV Batteries – A Game Changer?
- What is a CT Clamp and Does My Charger Need One?
- Is Using an EV Granny Charger Safe?
- Charge Rage: Is It Really a Thing?
- Vehicle to Load (V2L): What It Is & How It Works
- 16 Top Charge Point Operators in the UK
- 8 Types of EV Battery Explained
- Where Can I Charge My Electric Car?
- Electric Car Maintenance and Servicing Guide
- How Often Should I Charge My Electric Car?
- How to Check EV Battery Health
- Do Electric Cars Pay Road Tax?
- October 2024 Budget: Key EV News
- EV vs ICE – Which is Best?
- Should I Charge My EV to 80 or 90 or 100%?
- UK Government Announces Hybrid Sales Allowed Until 2035
- BEV vs PHEV – What’s the Difference?
- Definitely Not A Guru (Jim Starling) Reviews Joosup
- How Long Do Electric Car Batteries Last?
- 25 New Electric Car Brands on UK Roads